Bootstrap Textarea Placeholder
Overview
Inside the webpages we make we apply the form features to get several details from the website visitors and return it back to the site founder completing different goals. To complete it correctly-- suggesting obtaining the proper replies, the appropriate questions needs to be asked so we architect out forms form with care, thinking of all the achievable circumstances and types of information needed and actually provided.
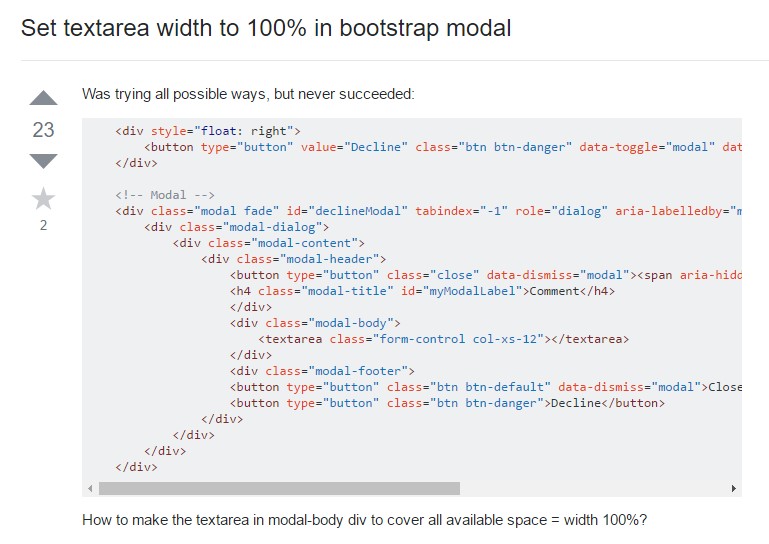
And yet no matter exactly how accurate we operate in this, there regularly are some scenarios when the relevant information we require from the site visitor is quite blurry before it gets in fact provided and needs to spread over much more than simply the standard a single or a handful of words generally written in the input fields. That is really where the # element shows up-- it's the only and irreplaceable element in which the visitors have the ability to easily write back a number of lines providing a comments, providing a good reason for their actions or simply just a handful of notions to eventually help us producing the product or service the web page is about much much better. ( more helpful hints)
The best ways to make use of the Bootstrap textarea:
Located in current edition of the most famous responsive framework-- Bootstrap 4 the Bootstrap Textarea Placeholder element is fully supported instantly adapting to the size of the display screen web page becomes shown on.
Generating it is quite straightforward - all you need is a parent wrapper
<div>.form-grouplabel<textarea>for = “ - the textarea ID - "Next we need to build the
<textarea>.form-controlfor = ""<label><textarea>rows=" ~ number ~ "<textarea>Given that this is certainly a responsive element by default it extends the whole size of its parent element.
A bit more hints
On the other side of coin-- there are really several circumstances you would prefer to limit the responses supplied within a
<textbox>maxlenght = " ~ some number here ~ "For examples
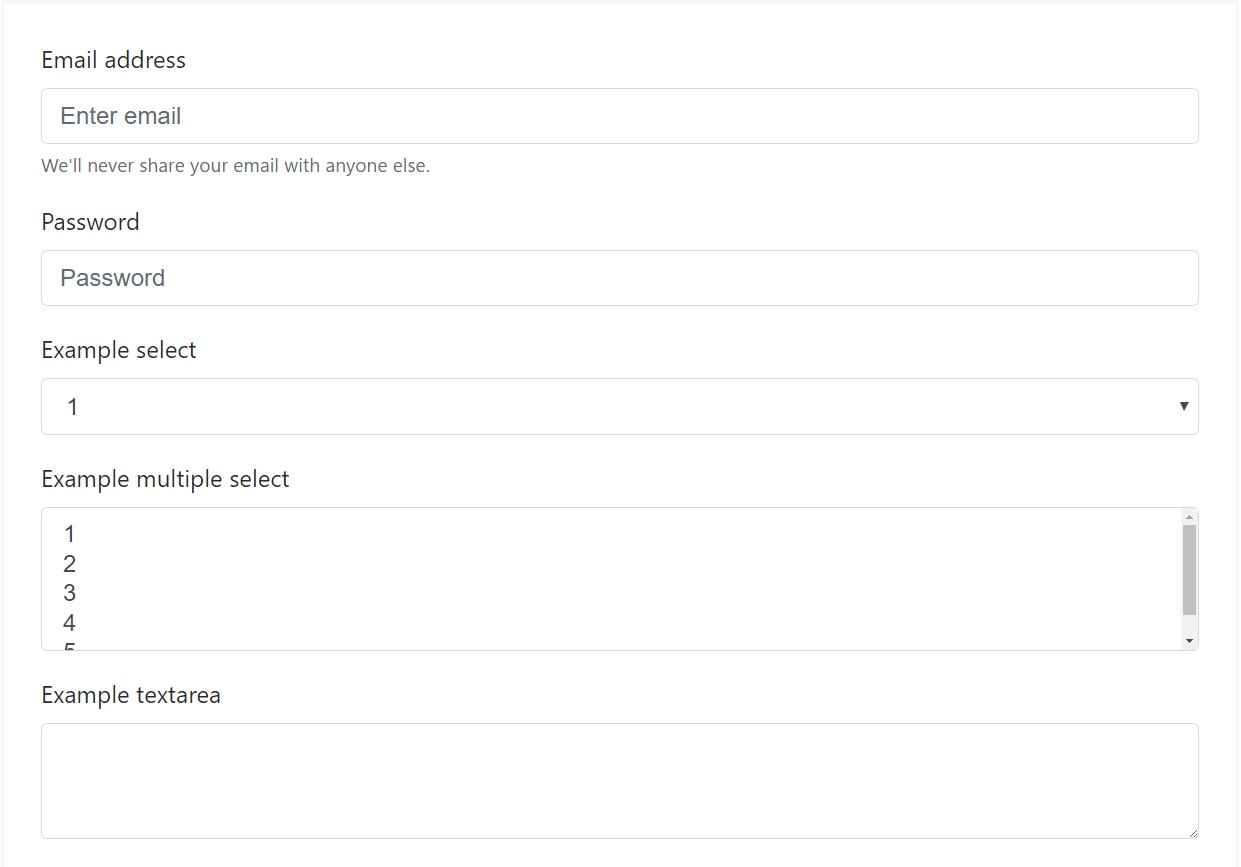
Bootstrap's form controls expand on Rebooted form styles with classes. Operate these particular classes to opt right into their modified displays for a even more regular rendering throughout browsers and gadgets . The example form listed below demonstrates typical HTML form elements that gain improved designs from Bootstrap with added classes.
Always remember, considering that Bootstrap applies the HTML5 doctype, all of the inputs must have a
type<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">Email address</label>
<input type="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" aria-describedby="emailHelp" placeholder="Enter email">
<small id="emailHelp" class="form-text text-muted">We'll never share your email with anyone else.</small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">Password</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect1">Example select</label>
<select class="form-control" id="exampleSelect1">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleSelect2">Example multiple select</label>
<select multiple class="form-control" id="exampleSelect2">
<option>1</option>
<option>2</option>
<option>3</option>
<option>4</option>
<option>5</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleTextarea">Example textarea</label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="exampleTextarea" rows="3"></textarea>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">File input</label>
<input type="file" class="form-control-file" id="exampleInputFile" aria-describedby="fileHelp">
<small id="fileHelp" class="form-text text-muted">This is some placeholder block-level help text for the above input. It's a bit lighter and easily wraps to a new line.</small>
</div>
<fieldset class="form-group">
<legend>Radio buttons</legend>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios1" value="option1" checked>
Option one is this and that—be sure to include why it's great
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios2" value="option2">
Option two can be something else and selecting it will deselect option one
</label>
</div>
<div class="form-check disabled">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="radio" class="form-check-input" name="optionsRadios" id="optionsRadios3" value="option3" disabled>
Option three is disabled
</label>
</div>
</fieldset>
<div class="form-check">
<label class="form-check-label">
<input type="checkbox" class="form-check-input">
Check me out
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button>
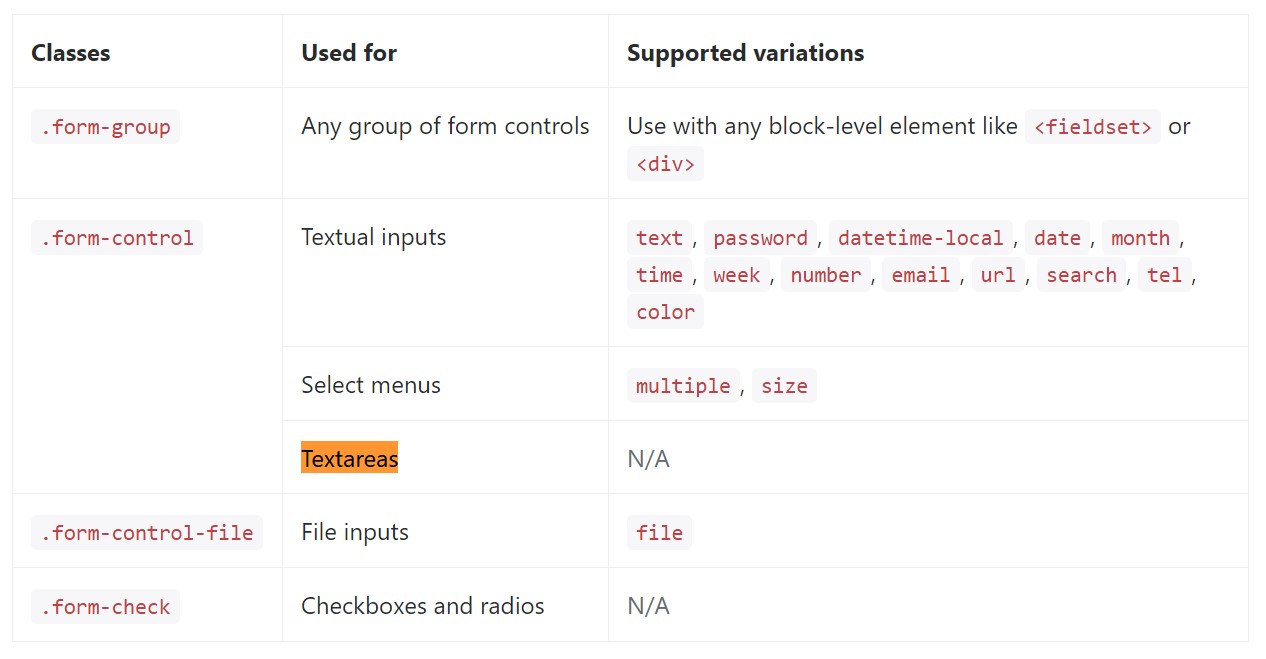
</form>Shown below is a total listing of the specific form controls maintained simply by Bootstrap plus the classes that modify them. Additional documentation is available for each and every group.
Final thoughts
So now you realize exactly how to develop a
<textarea>Check a couple of youtube video short training about Bootstrap Textarea Input:
Related topics:
Essentials of the textarea

Bootstrap input-group Textarea button using
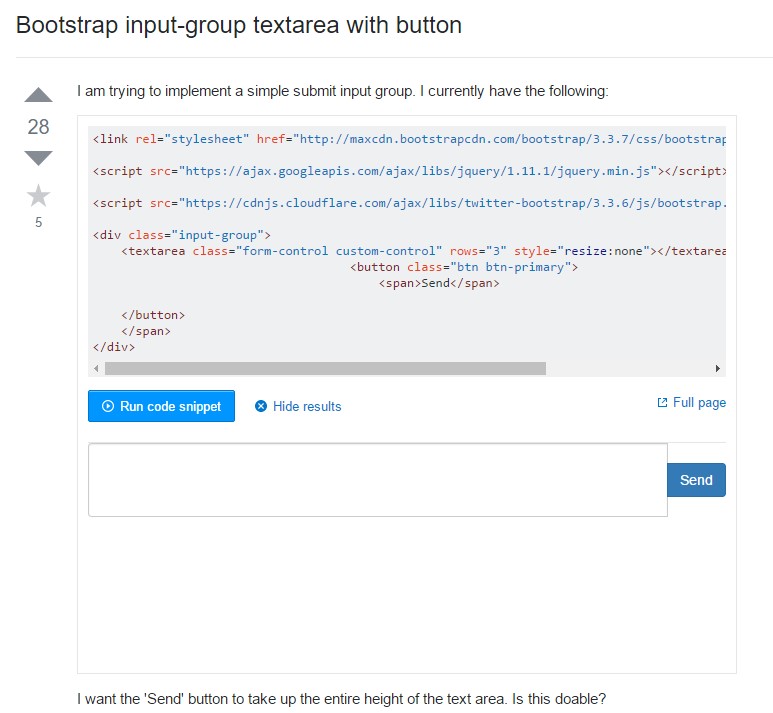
Install Textarea width to 100% in Bootstrap modal